New Jersey is home to many pests and diseases that want to attack your trees and plants. Effective prevention and treatment of pests and disease starts with identification.
Which Tree Pests and Diseases Do We Have in Northern New Jersey?
Want to know which creatures are after your trees and plants? Check out our extensive information below and check back for updates as new pest knowledge becomes available.
Call Aspen Tree for Identification & Treatment of Insect Pests & Diseases!
Still not sure which insect or disease is attacking your trees? Need help with prevention or treatment applications?
Call us today to schedule a complimentary assessment of your landscape. Our pest and disease experts will inspect your plants, identify any problems, and provide you with a program and estimate customized to treat your specific trees and shrubs.
Tree & Shrub Diseases in Northern New Jersey
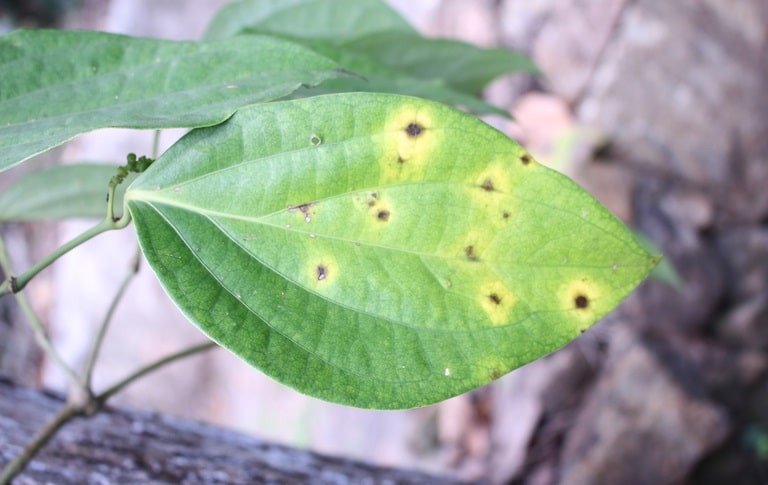

Anthracnose
(Colletotrichum lindemuthianum)
Anthracnose is a fungal condition caused by various fungi species of the Colletotrichum genus. Symptoms include leaf spotting and the development of cankers.
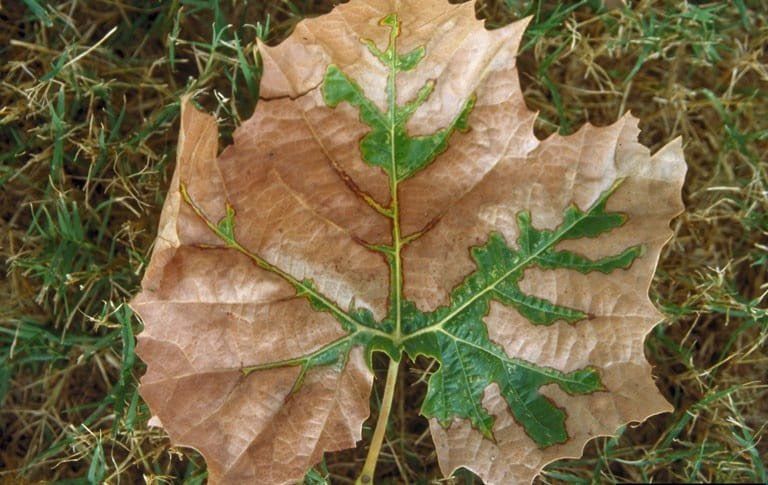

Bacterial Leaf Scorch
(Xylella fastidiosa)
The bacteria responsible for BLS invades the xylem tissue of plants, restricting water flow from the roots to the crown. Symptoms include premature leaf browning and early leaf drop.
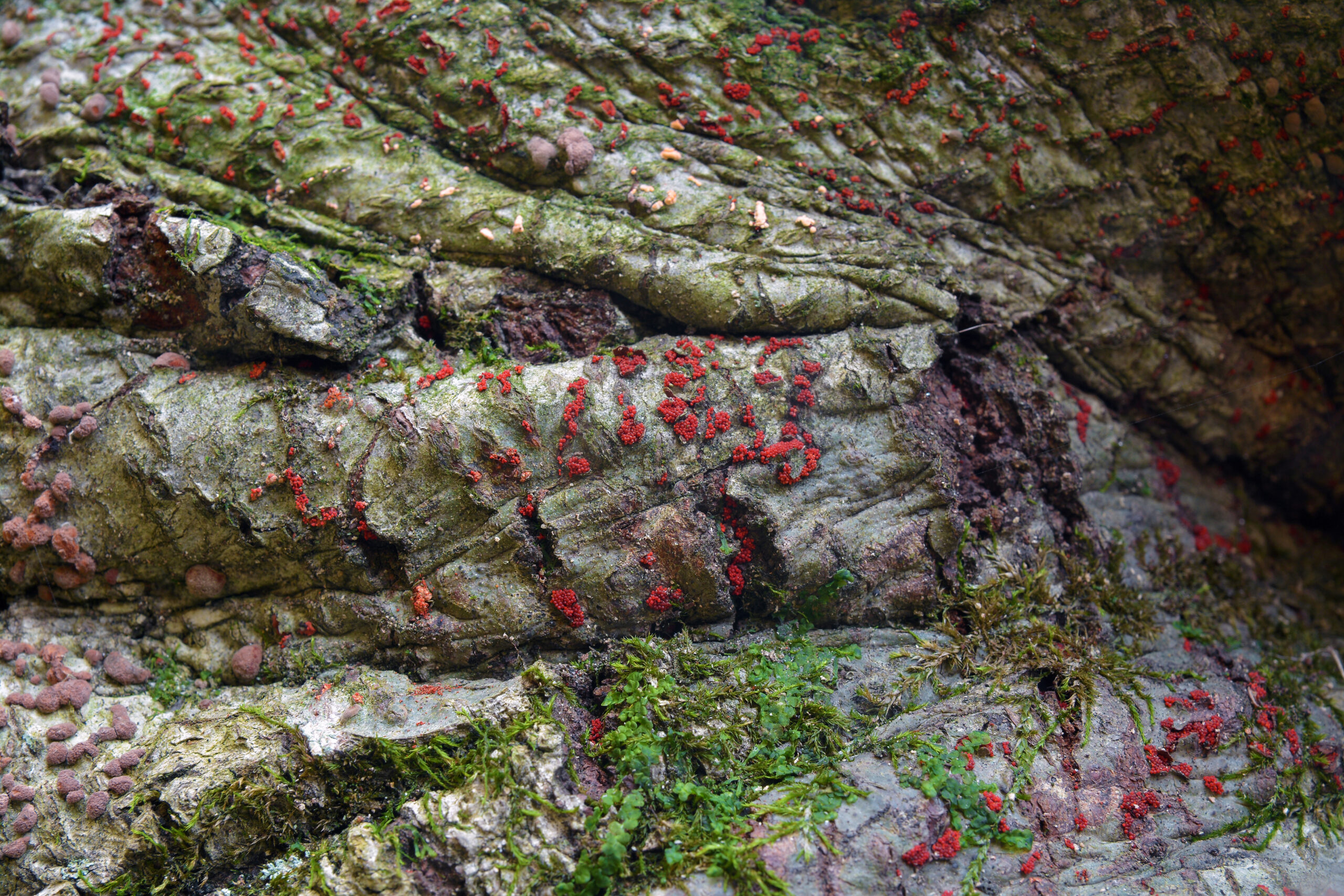

Beech Bark Disease
(Neonectria faginata & Cryptococcus fagisuga)
This disease involves a scale insect creating wounds that allow a fungus to enter and infect the tree. Symptoms include scale insects on the trees (that look like white wool), cankers, and a reduced canopy.
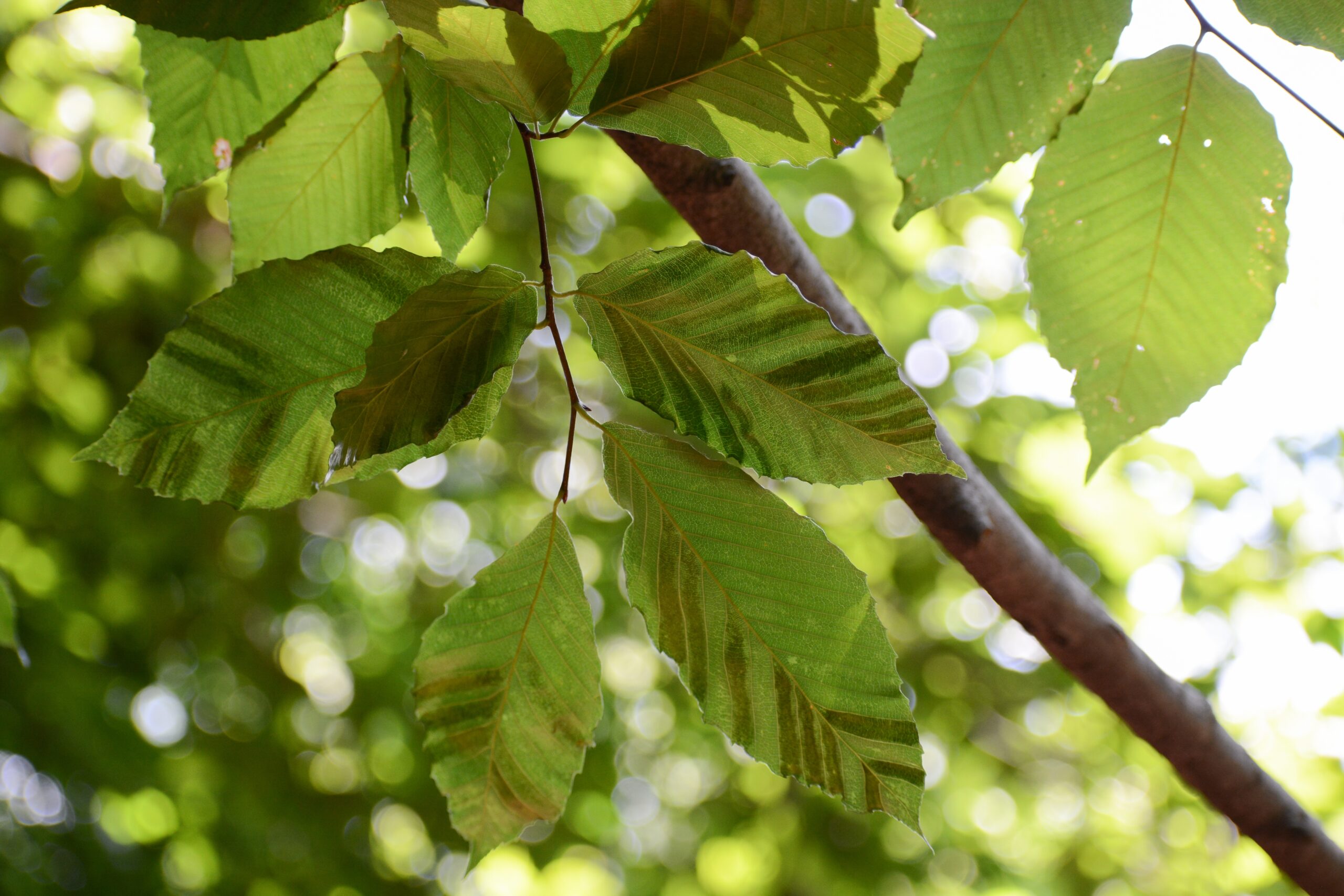

Beech Leaf Disease
(Litylenchus crenatae)
Beech leaf disease affects American and European beech. Symptoms begin with dark bands between leaf veins, progressing to leaf curling, reduced leaf size, and eventual tree mortality within 2-7 years.
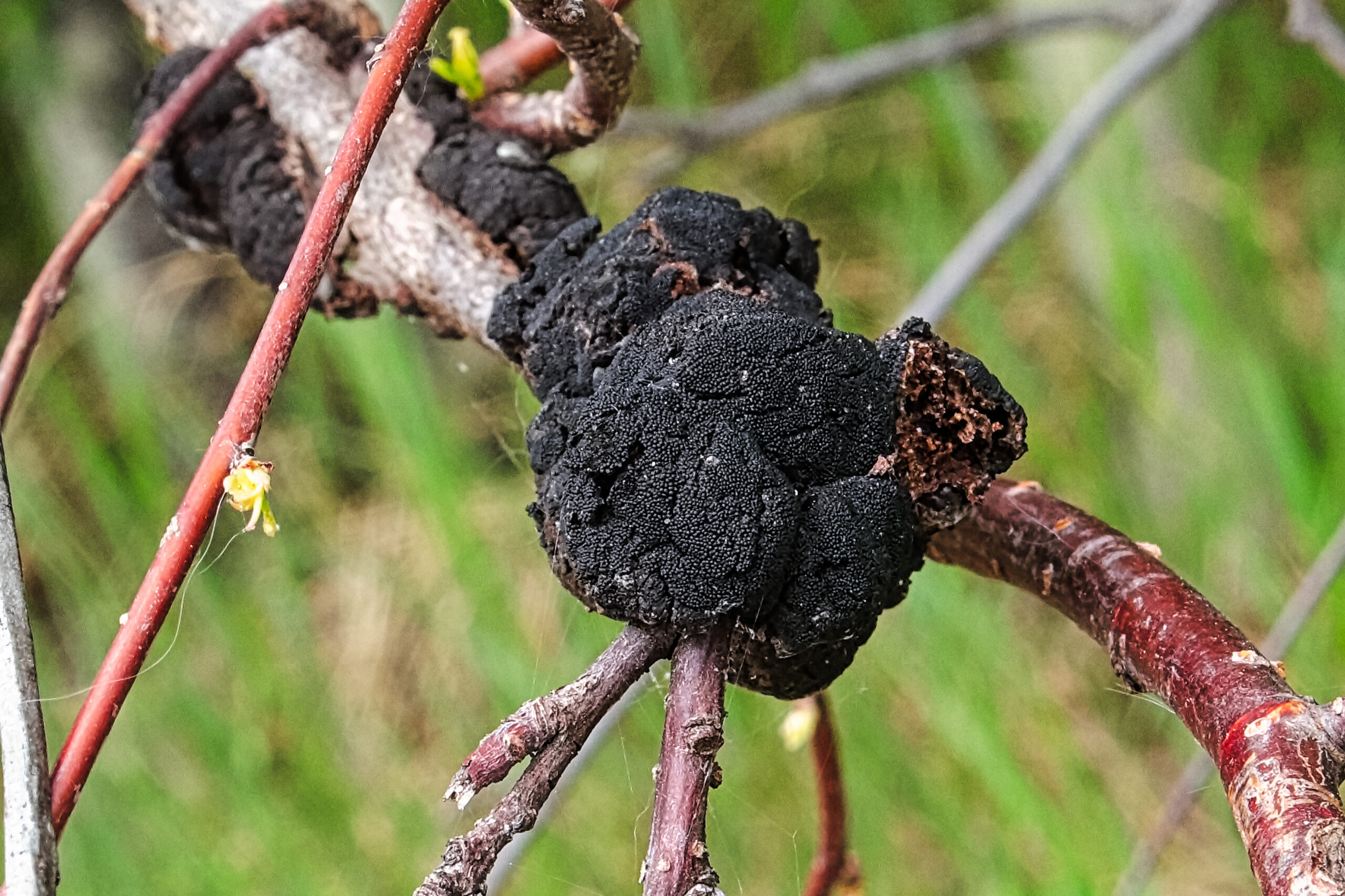

Black Knot
(Apiosporina morbosa)
A fungal disease affecting cherry, plum, and other Prunus species. The disease produces black galls on branches and the trunk. Some Prunus trees can tolerate black knot, while others are susceptible.
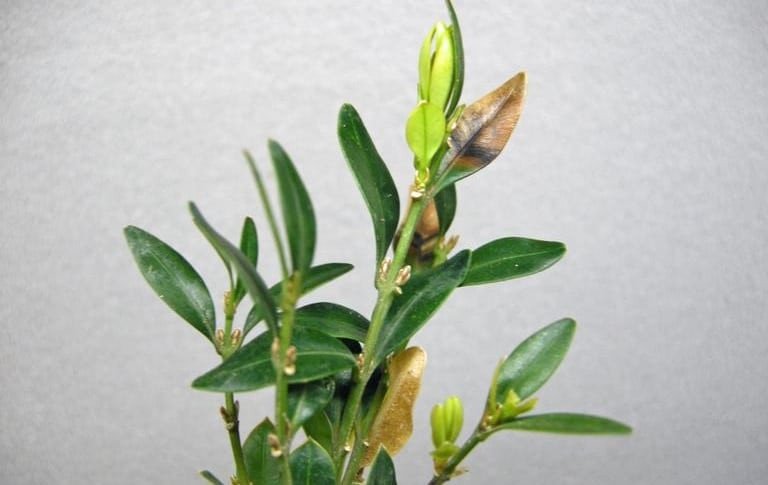

Boxwood Blight
(Calonectria pseudonaviculata)
Boxwood blight is a condition resulting from infection by Calonectria pseudonaviculata fungus. Symptoms of boxwood blight include leaf spots and blotches, defoliation, and lesions on plant stems.
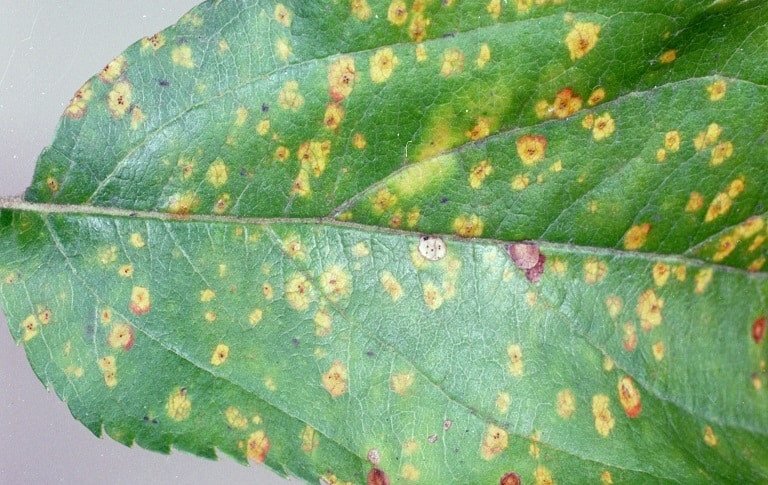

Cedar-Apple Rust / Hawthorn Apple Rust
(Gymnosporangium juniperi)
Another fungal disease, cedar apple rust, also known as hawthorn apple rust, most commonly affects species of apple and crabapple trees. Symptoms include green-yellow leaf spots that enlarge and turn brown and orange jelly-like galls.
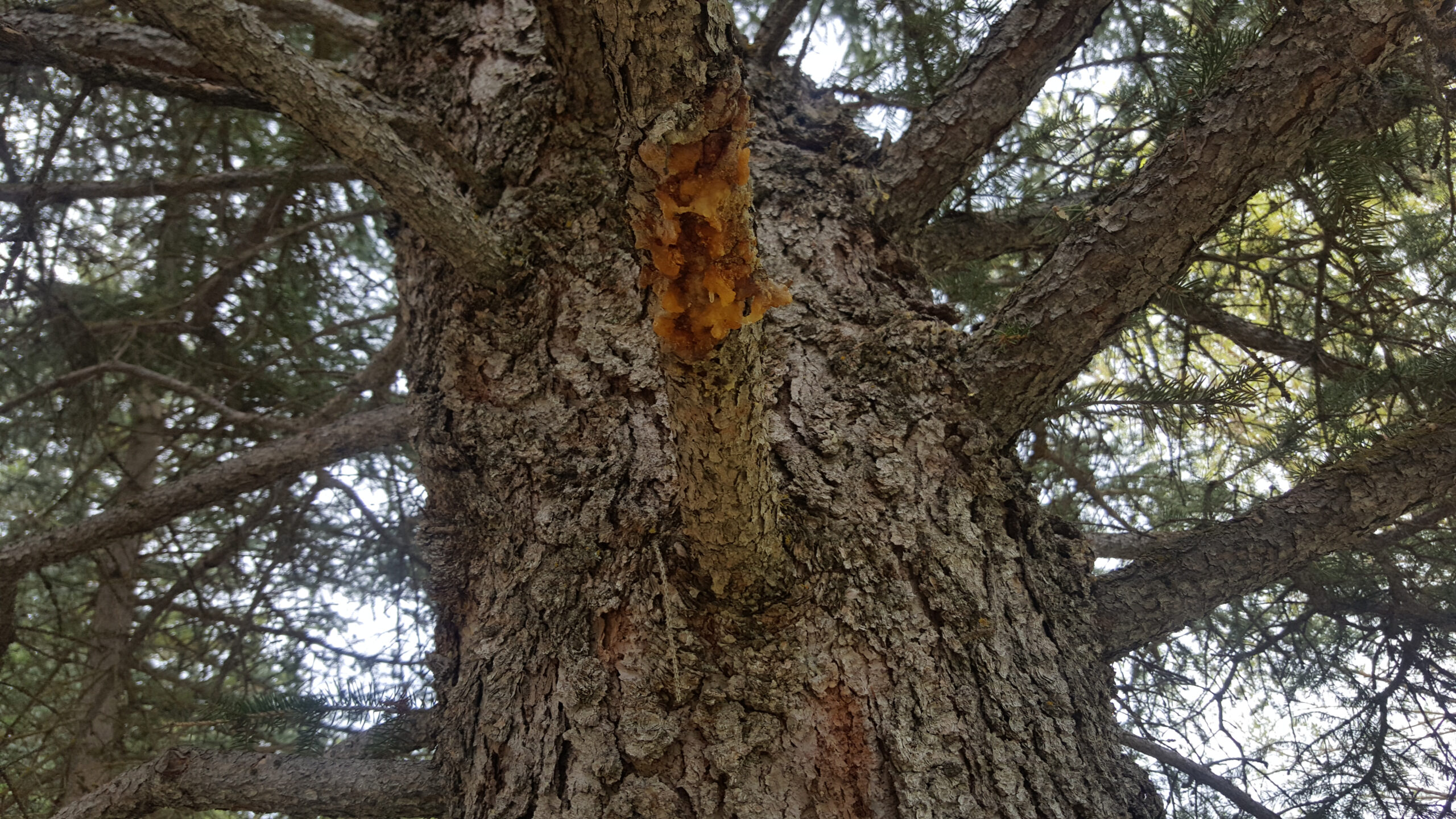

Cytospora Canker
(Cytospora spp.)
This fungal disease primarily affects stressed spruce trees. The disease will kill scattered branches throughout the canopy but will rarely kill the tree outright. Prune any dead branches as soon as possible.
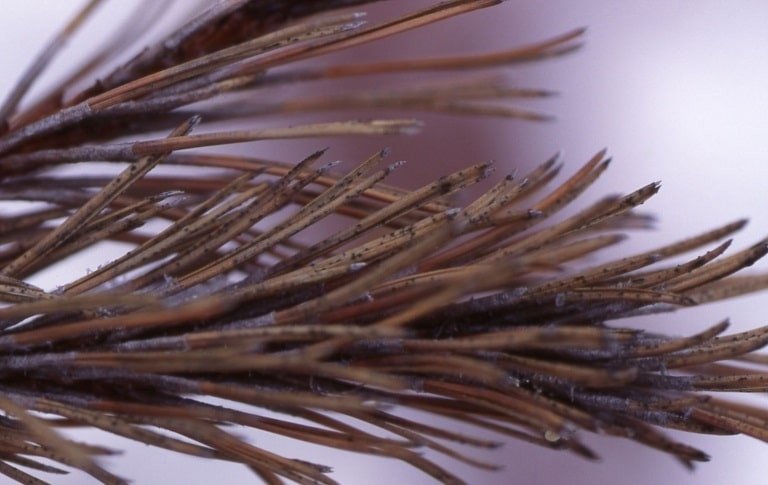

Diplodia Tip Blight
(Sphaeropsis sapinea)
Diplodia tip blight is a fungal disease that attacks stressed landscape pine trees. Symptoms include browning of the pine needles on branch tips. Branch die-off is common and repeated infections can result in the death of the tree.
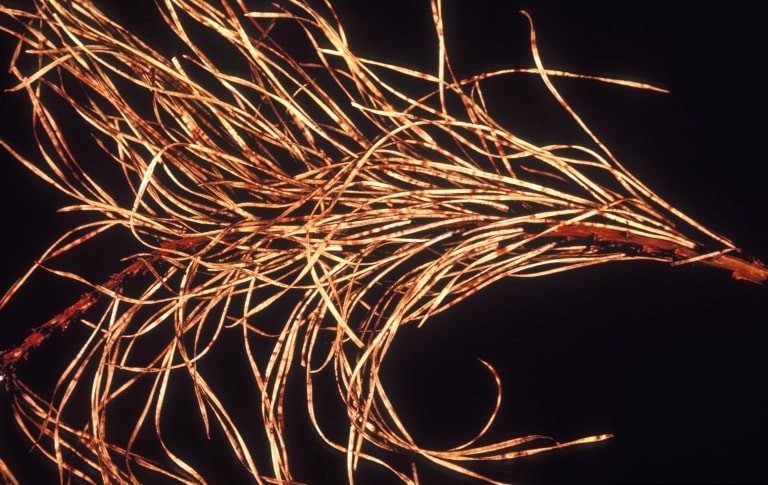
Dothistroma Needle Blight
(Dothistroma septosporum)
This fungal disease is slow moving with a lifecycle that takes a full year to complete. Symptoms include the browning of needles with repeated infections severely damaging the tree canopy.
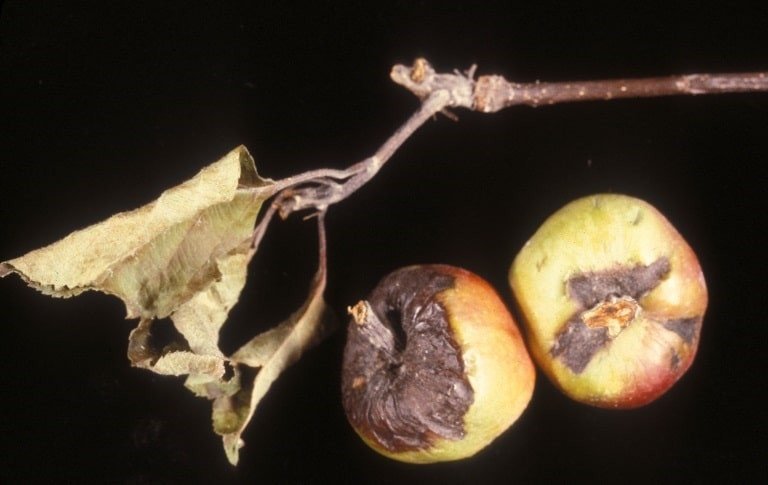

Fireblight
(condition caused by Erwinia amylovora)
The highly contageuous Erwinia amylovora bacteria causes dying branch tips in apple, pear, and crab apple trees. It also attacks shoots, leaves, branches, fruits, and roots of infected trees.

Oak Wilt
(Bretziella fagacearum)
Oak wilt is a devastating fungal disease that affects red and white oaks. Symptoms include wilting and bronzing of leaves from the top of the tree downward, followed by rapid leaf drop and tree death.

Phytophthora Root Rot
(Phytophthora spp.)
This disease occurs due to fungi in the water when there are periods of rain. Symptoms include leaves looking drought-stressed and darkening of the bark around the soil line.
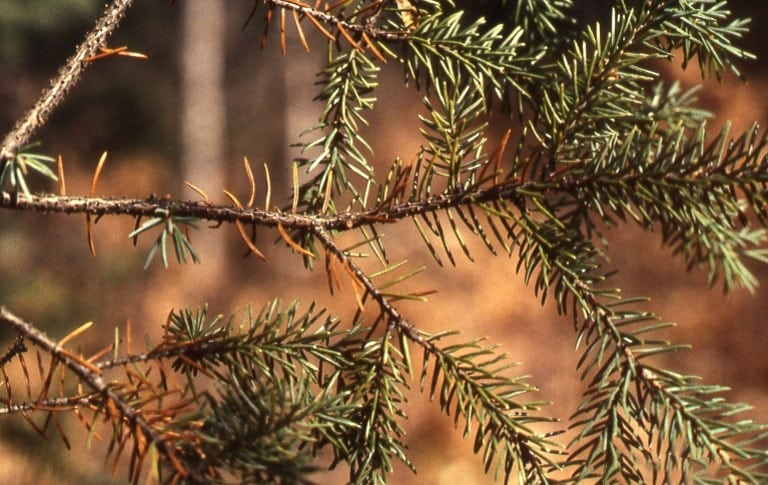

Rhizosphaera Needlecast
(Rhizosphaera kalkhoffi)
Spruce trees suffering from heat stress and poor planting are especially at risk from this fungal disease. Symptoms include needle death and premature needle drop.
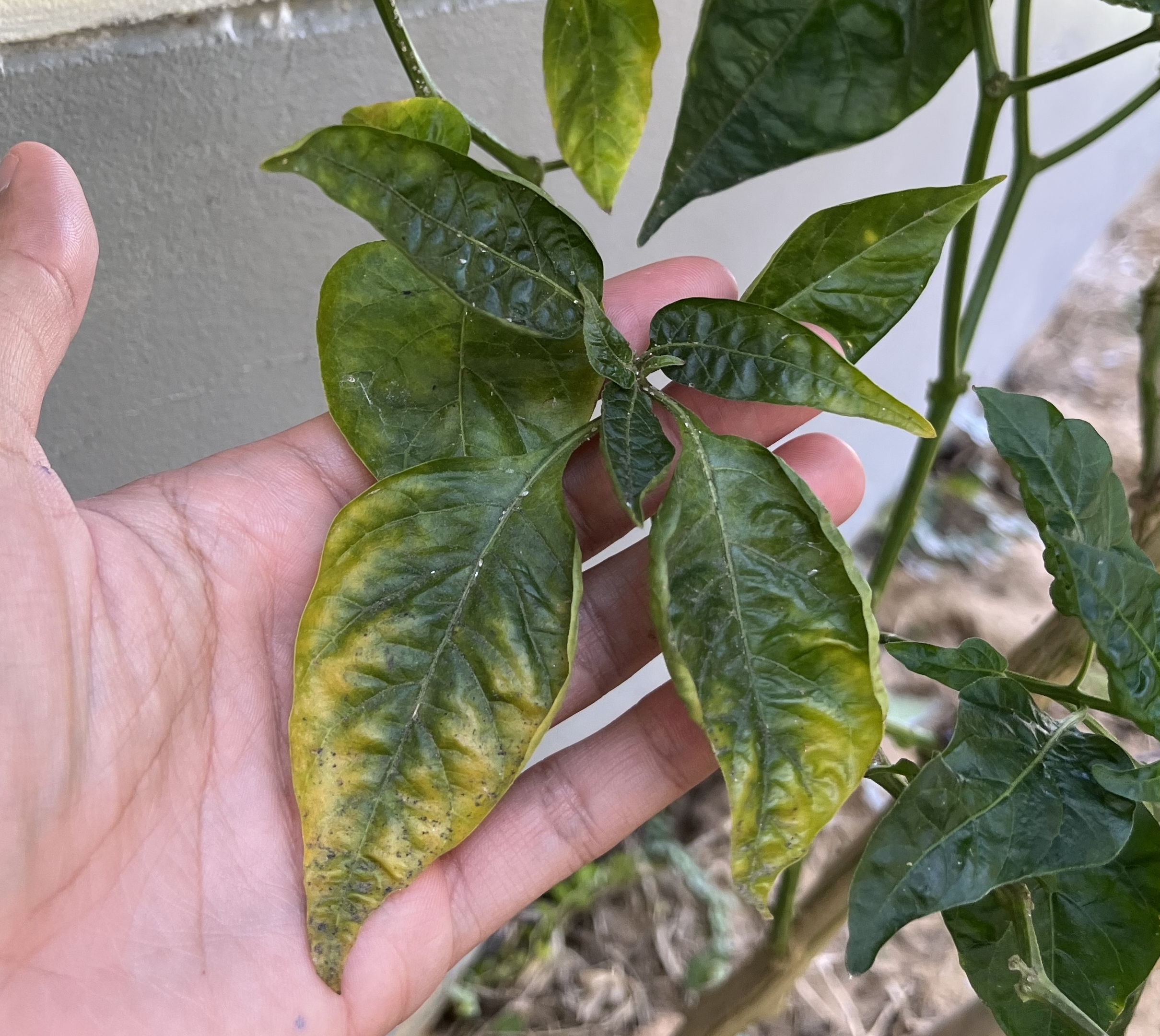

Verticillium Wilt
(Verticillium dahliae & V. albo-atrum)
This soil-borne fungal disease affects over 300 plant species, including maple, elm, and ash trees. Symptoms include sudden wilting of branches, leaf yellowing, and leaf browning.
Insect Pests of Trees & Shrubs in Northern NJ
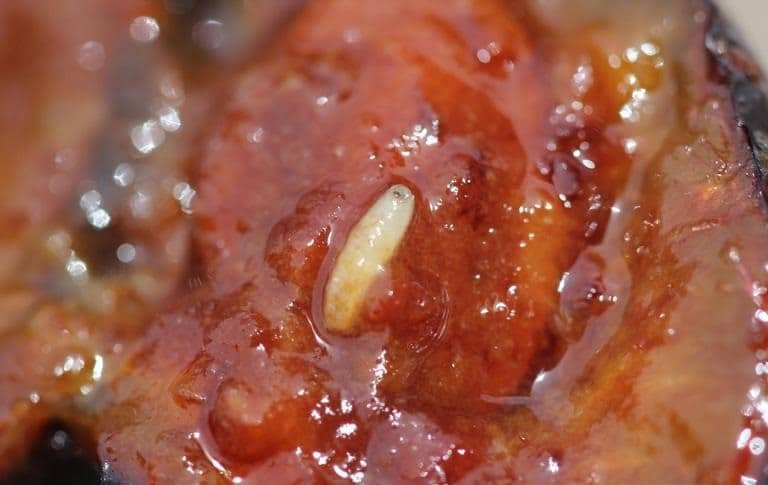
Apple Maggot
(Rhagoletis pomonella)
Also called the apple maggot fly or railroad worm, this insect is a pest of cultivated apples and is native to North America.
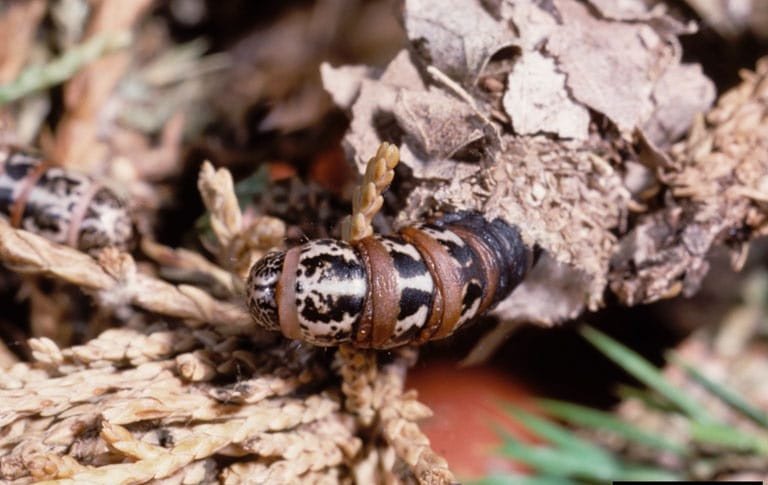

Bagworm
(Thyridopteryx ephemeraeformis)
A native pest, the bagworm is a defoliating caterpillar that causes most of its damage in urban and suburban areas. The extent of the damage ranges from the weakening of affected plants to plant death.
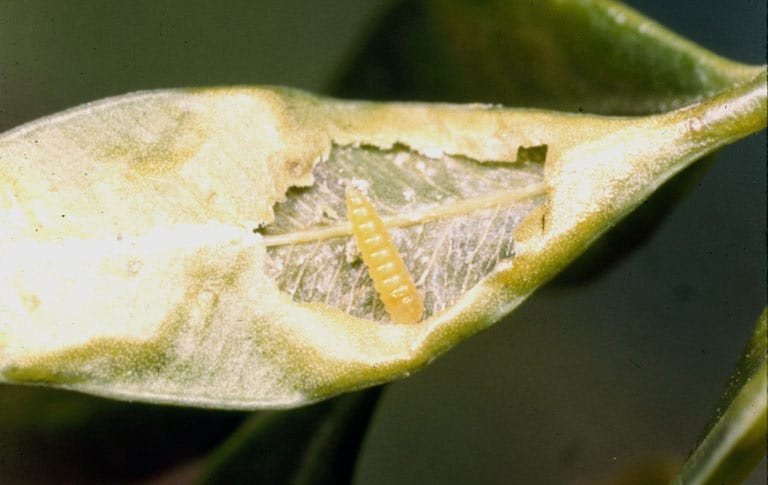

Boxwood Leafminer
(Monarthropalpus flavus)
An invasive pest from Europe, this small fly lays eggs in the underside of leaves. Upon hatching, the leafminer maggots begin mining the insides of the leaves as they feed.
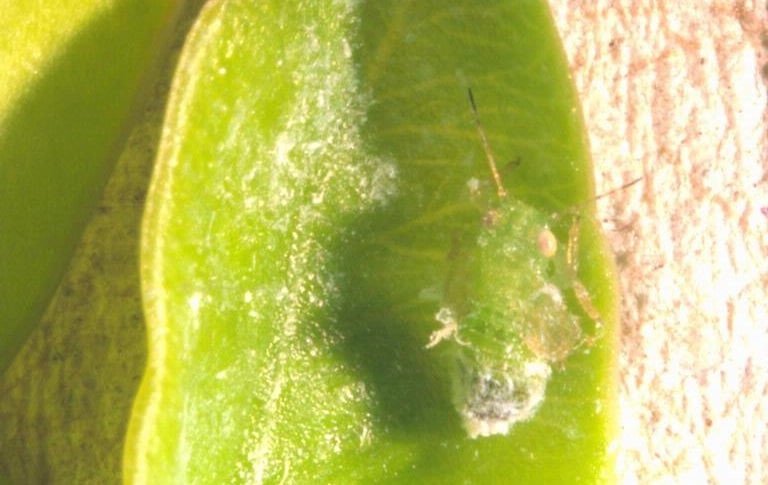

Boxwood Psyllid
(Psylla buxi)
This sap-sucking insect pest feeds primarily on the common box (Buxus sempervirens), but all boxwood species are susceptible.
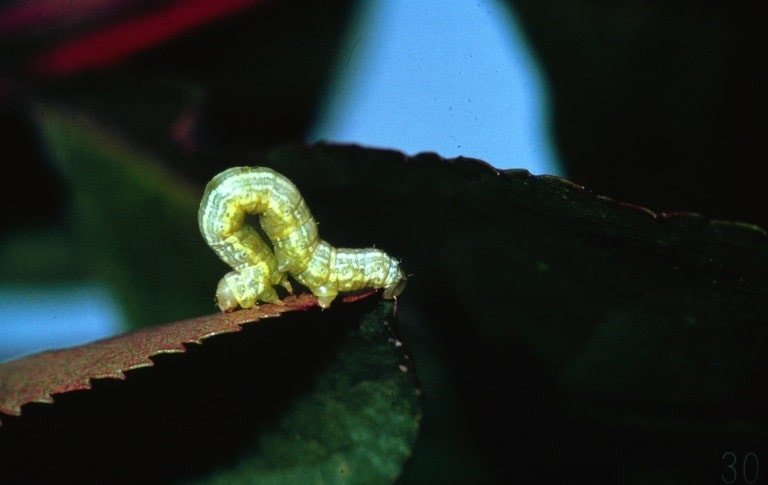

Canker Worm
(Alsophila pometaria & Paleacrita vernata)
The larval form of the adult moth, the fall (A. pometaria) and the spring (P. vernata) canker worms are both found in North America and are known to feed on multiple shrub species of the Acer, Ulmus, Betula, and Prunus species.

Codling Moth
(Cydia pomonella)
Believed to have been introduced from Europe, this moth is a common orchard pest whose larvae feed on fruits including apples, peaches, and pears.
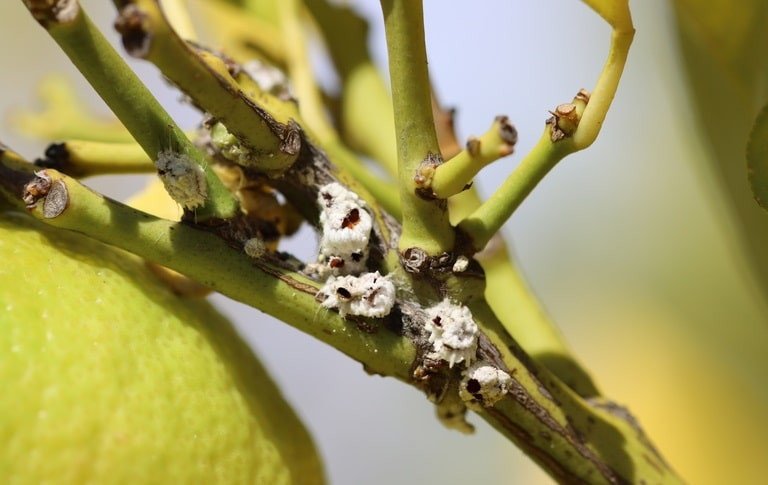

Cottony Cushion Scale
(Icerya purchasi Maskell)
Introduced to California from Australia, this insect pest affects a number of host plants including apple, boxwood, cypress, hackberry, locust, maple, oaks, peaches and plums (Prunus), pecan, pears, pine, rose, verbena, walnut, willow and other woody ornamentals.
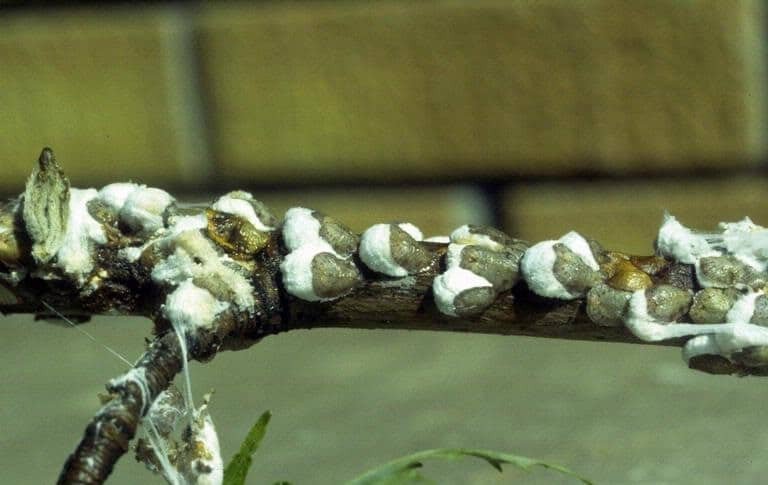

Cottony Maple Scale
(Pulvinaria innumerabilis)
Native to North America, this insect pest can kill trees in high enough numbers and has a number of hosts including honey locust, black locust, white ash, euonymus, oak, boxelder, dogwood, hackberry, sycamore, linden, beech, elm, willow, basswood, poplar, rose and sumac.
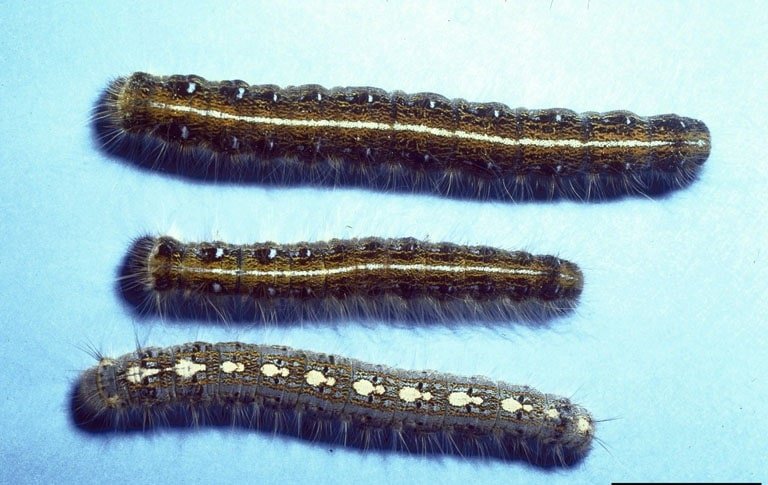

Eastern Tent Caterpillar
(Malacosoma Americanum)
Native to North America, these leaf-eating caterpillars can easily defoliate an entire tree. Outbreaks occur every few years as the populations of this pest fluctuate.
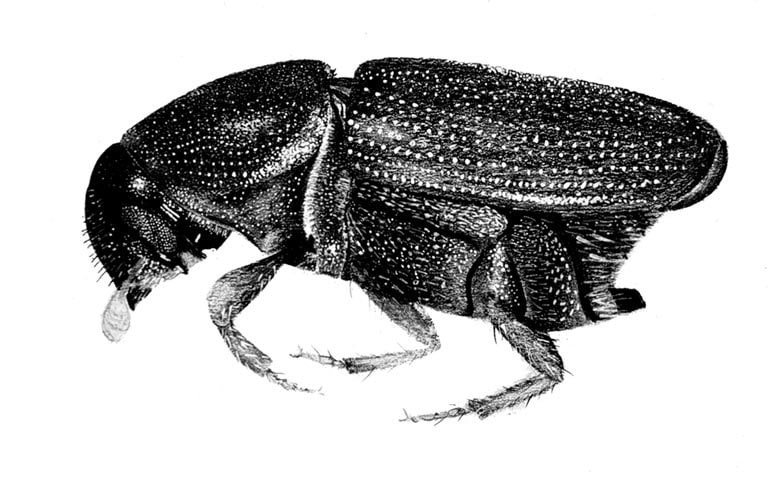
Elm Bark Beetle
(Hylurgopinus rufipes)
The larvae are small, white, and grub-like and are found under the bark of dying or dead elms. This bark beetle is native to North America and is best known as a vector of Dutch elm disease.
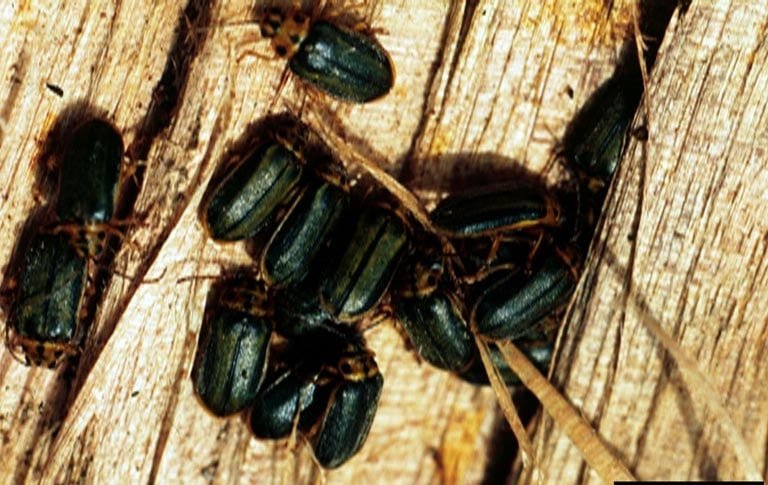

Elm Leaf Beetle
(Xanthogaleruca luteola)
This invasive beetle from Europe is widespread in North America. Adults and larvae feed on and skeletonize leaves of multiple elm species including the English elm, American elm, white elm, Siberian elm, and Chinese elm.
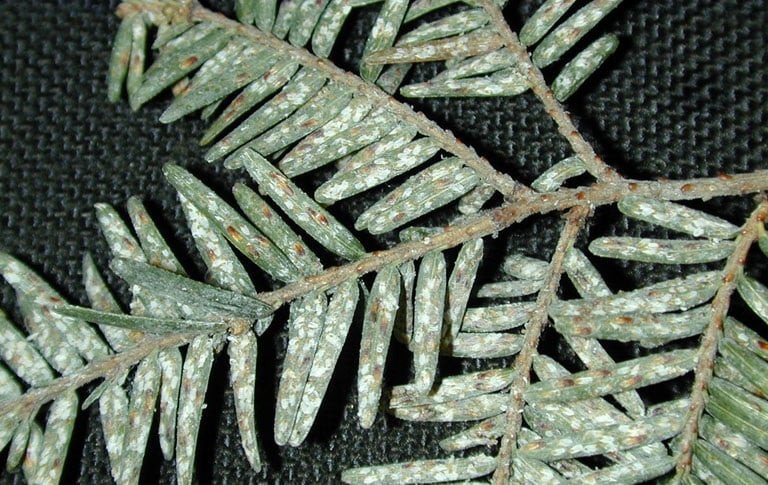

Elongate Hemlock Scale
(Fiorinia externa)
Also known as fiorinia scale, this Japanese native pest affects forest and ornamental hemlock trees in New Jersey.
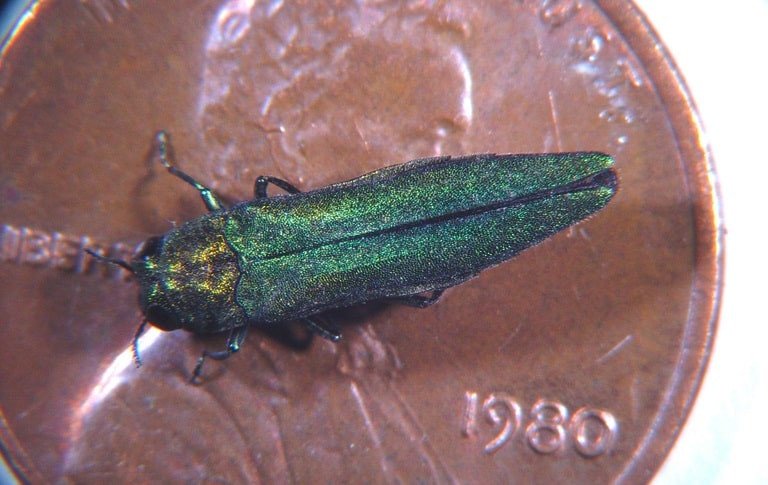

Emerald Ash Borer
(Agrilus planipennis)
An invasive pest from Asia, this beetle species attacks ash trees across the country. Once infested with EAB, ash trees die quickly.
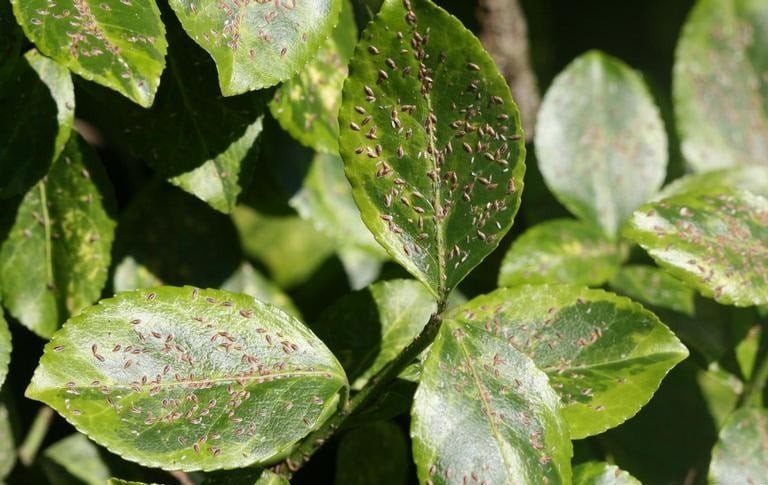

Euonymus Scale
(Unaspis euonymi)
Native to China and Japan, this pest affects several Euonymus species, Pachysandra species, and Celastrus species. Vine-type euonymus are especially susceptible to this scale insect.
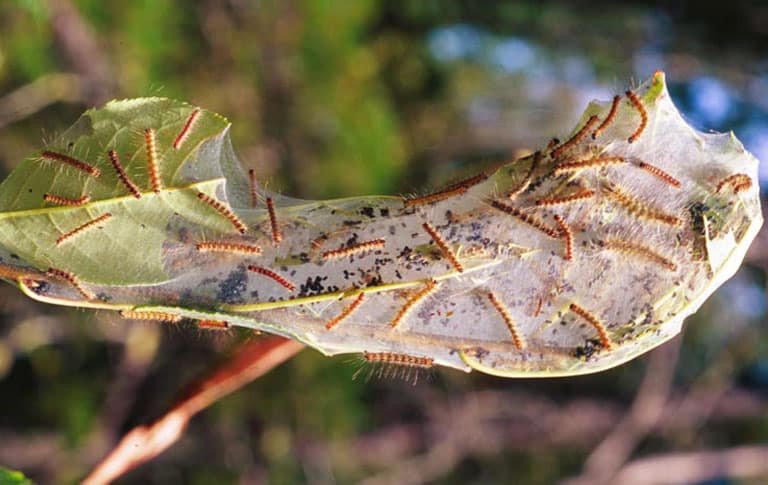

Fall Webworm
(Hyphantria cunea)
The larvae of this moth is a pest of various shrubs, ornamentals and trees. Native to the United States, this webworm was introduced to Yugoslavia from where it spread to much of Europe.
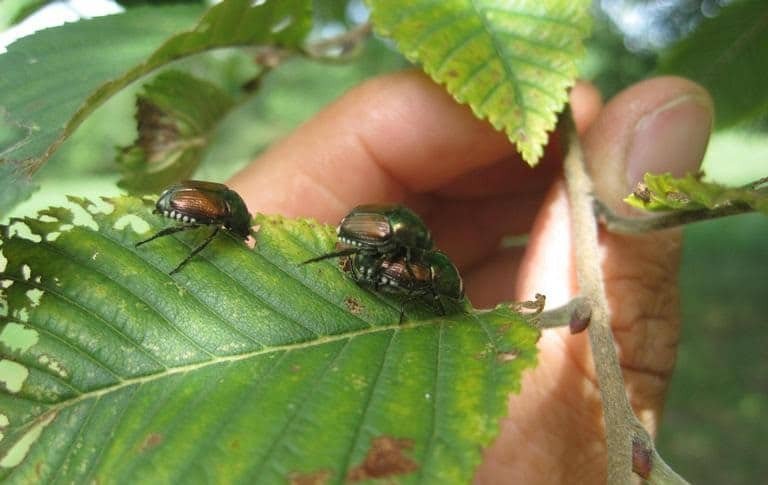

Japanese Beetle
(Popillia japonica)
An extremely destructive pest, these invasive beetles quickly devour leaves, giving them a lace-like appearance. They are non-specialist and are known to attack over 300 tree and plant species.
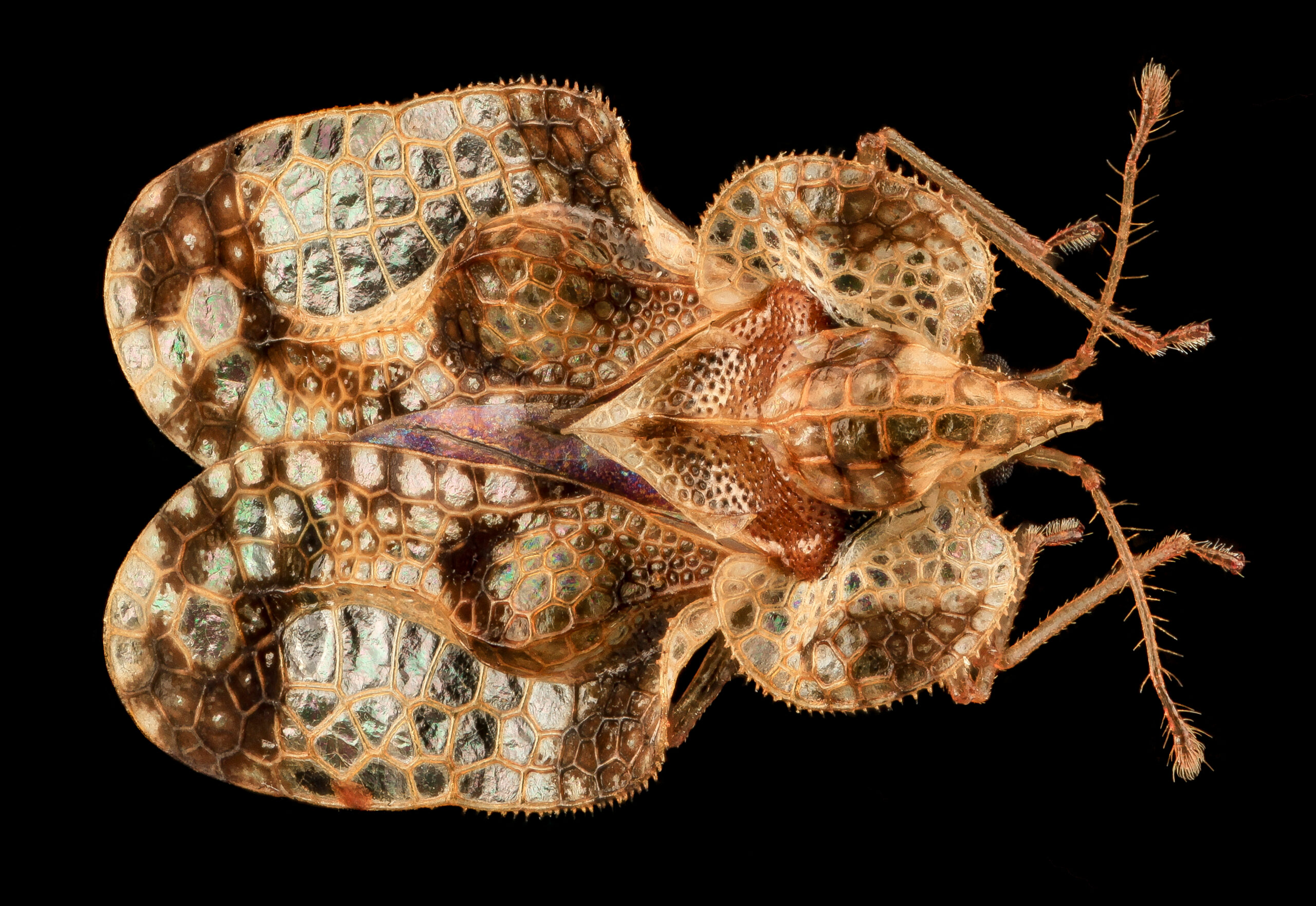
Lacebug
(Corythucha species)
These tiny insects with lace-like wings feed on the undersides of leaves by piercing and sucking plant fluids. Symptoms include stippling or bleaching of upper leaf surfaces and black fecal spots on leaf undersides.
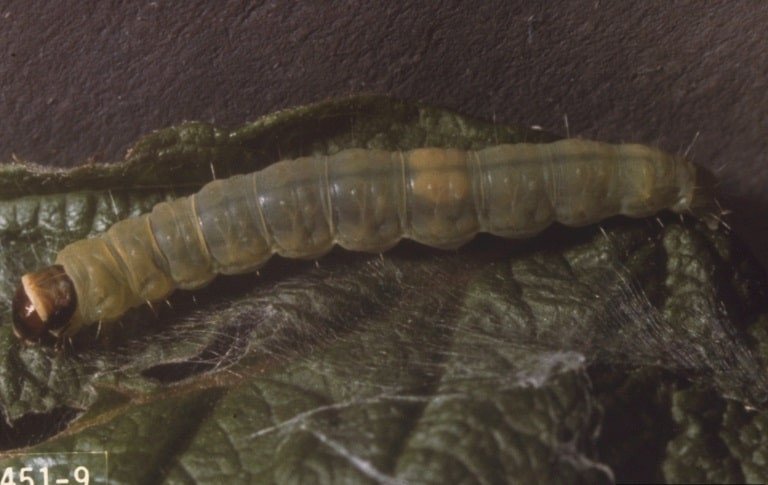

Leaf Roller
(family Tortricidae)
A large group of larvae in the Tortricidae family, the leaf-roller or bell moth are among the most destructive North American tree and shrub pests. They are named for the leaf rolling habit of the larvae.
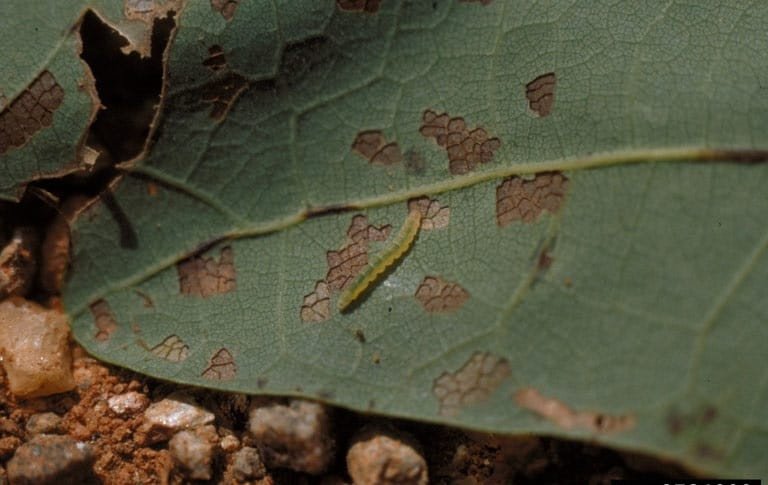

Oak Leaf Skeletonizer
(Bucculatrix ainsliella)
With two generations per year, the North American native oak leaf skeletonizer is a prolific pest, named for its feeding pattern of skeletonizing oak leaves.
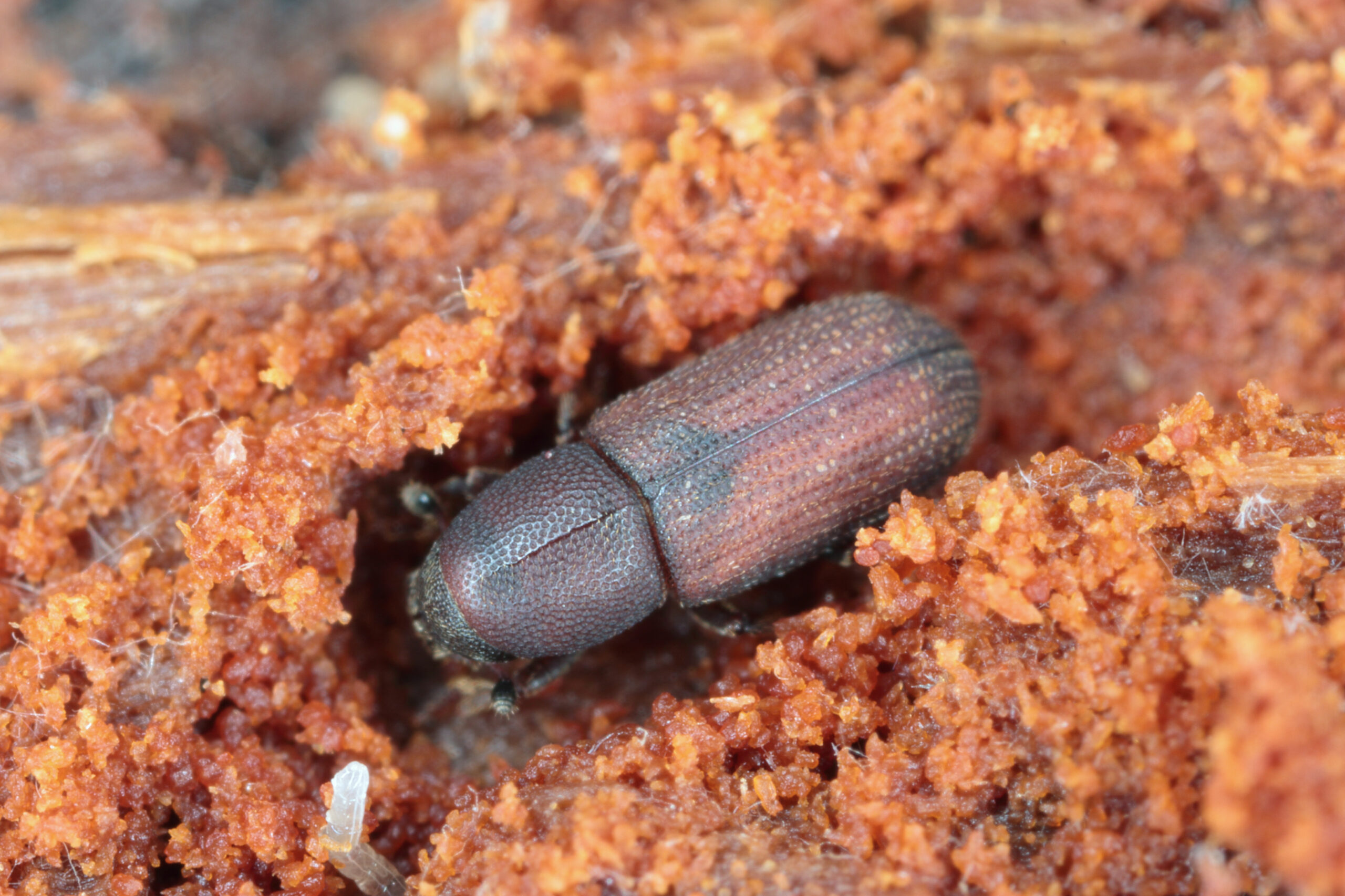

Pine Bark Beetle
(Dendroctonus & Ips species)
These native beetles attack stressed or weakened pine trees, boring through the bark to create egg galleries. Symptoms include pitch tubes on the trunk and sawdust at the base of trees.
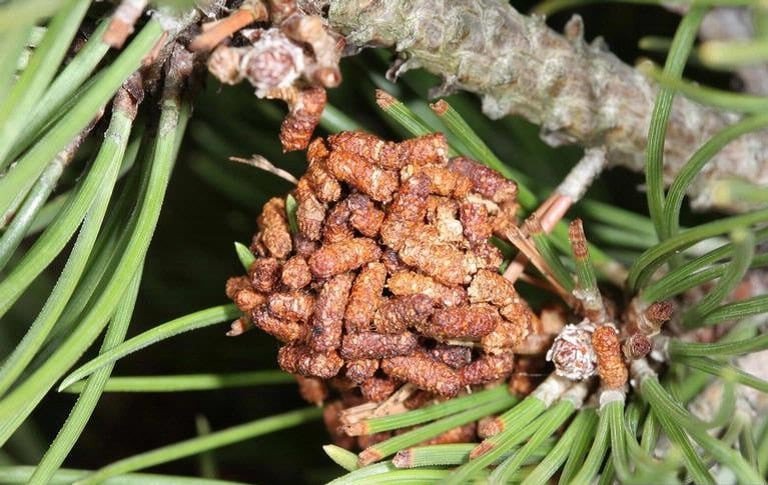

Pine False Webworm
(Acantholyda erythrocephala)
The invasive pine false webworm was first identified in North America in 1961. While initially affecting only immature white and red pines, larger scale infections on mature pines have been identified since 1993.
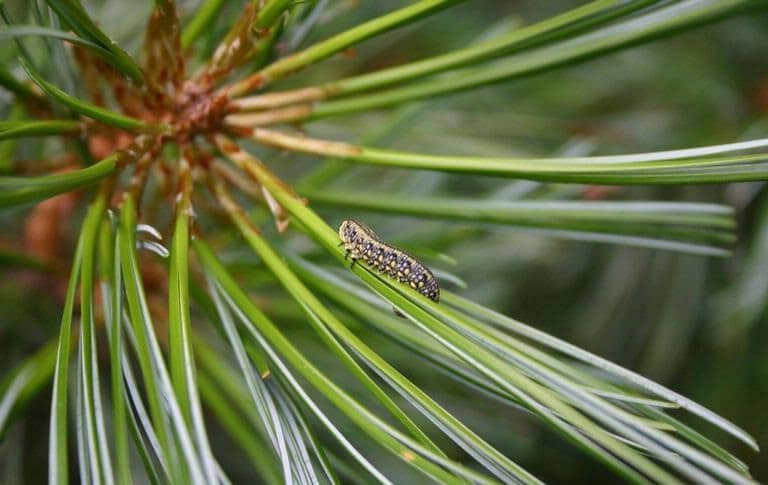

Pine Sawfly
(Neodiprion sertifer)
This conifer pest is known for defoliating pines in localized or regional outbreaks lasting one or more years. The European pine sawfly, introduced to the US in 1925, is the most common pine sawfly in New Jersey.
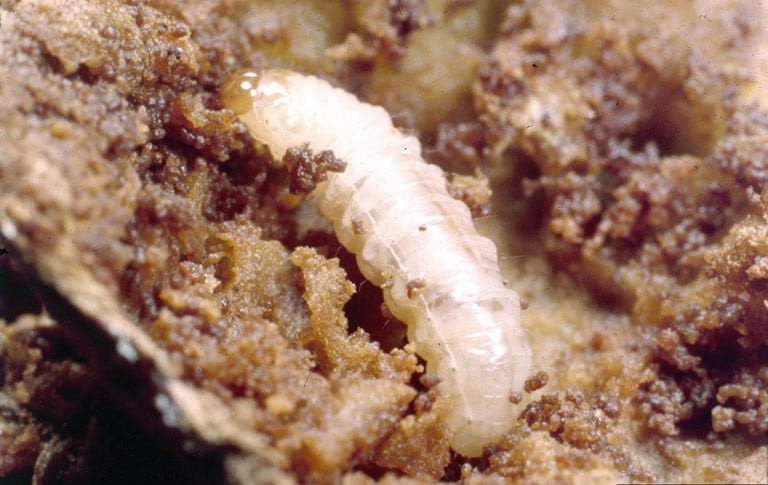

Plum Curculio
(Conotrachelus nenuphar)
This snout beetle species is native to North America. Adults feed on trees before females lay eggs on apples, peaches, and other fruits which the larvae then feed on until pupating underground in the fall.
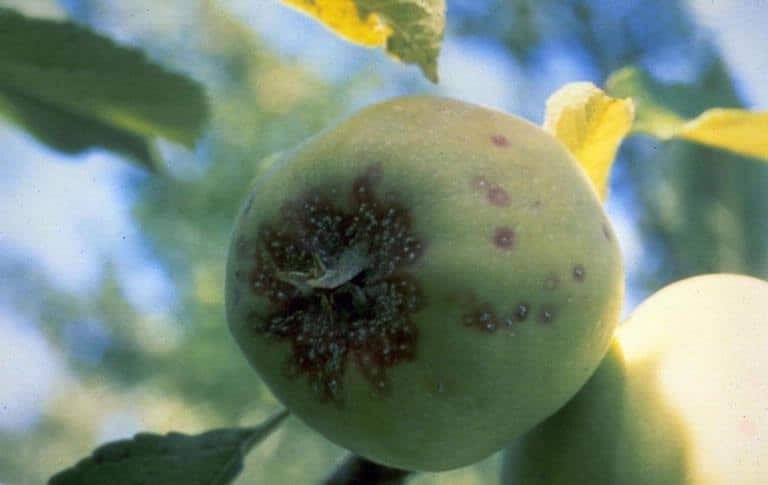

San Jose Scale
(Quadraspidiotus perniciosus)
Originally from China, this invasive scale insect was first identified in California and later accidently transported to Virginia and later New Jersey. Heavy infestations by these sucking pests can result in tree death.
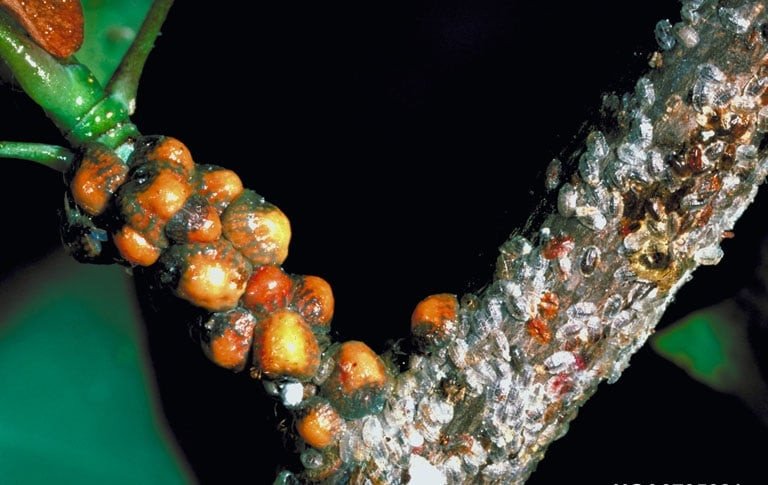

Scale Insects
(superfamily Coccoidea)
This diverse insect group uses their piercing mouthparts to suck sap from trees resulting in yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and even death of the host.
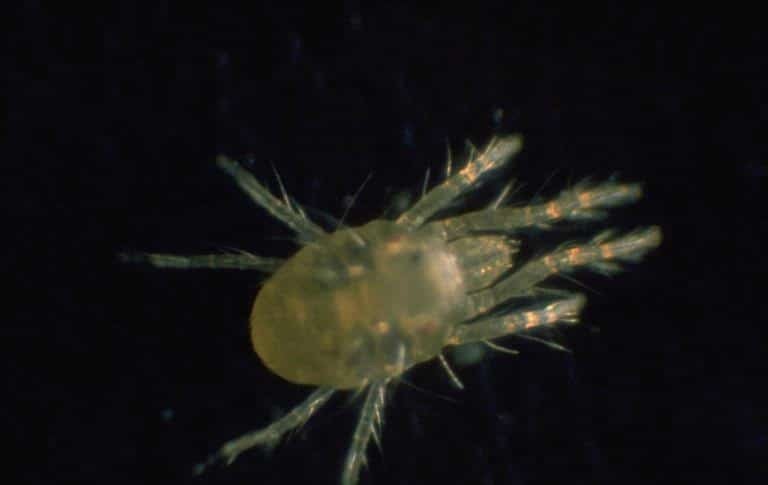

Spider Mites
(Tetranychus urticae)
These tiny sap-sucking pests are more closely related to spiders than insects. They are identifiable by the silk webbing they leave on the underside of leaves.
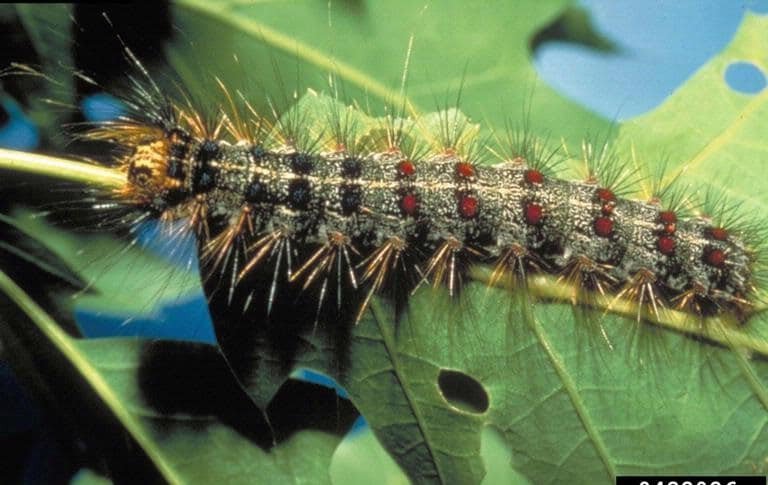

Spongy Moth / Gypsy Moth
(Lymantria dispar)
An invasive European moth, the spongy moth (formerly the gypsy moth) is a defoliator that interferes with a trees ability to perform photosynthesis.
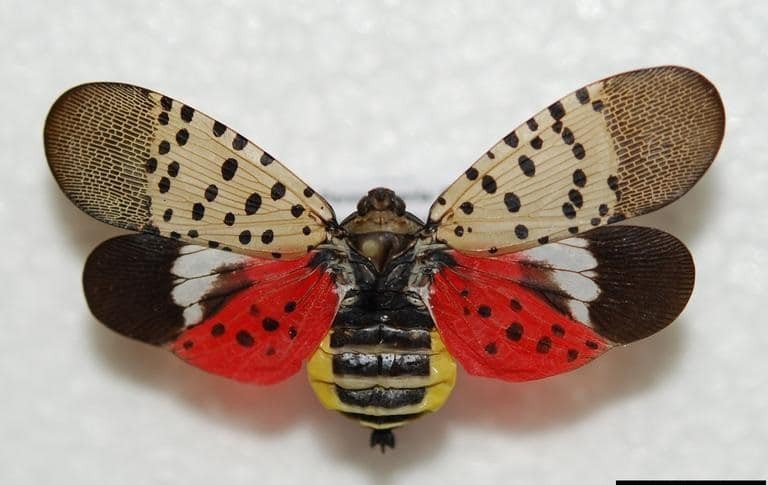

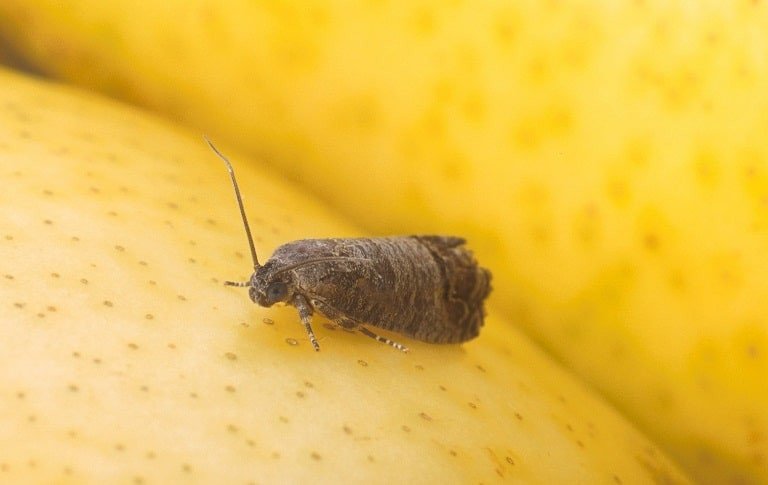
Spotted Lanternfly
(Lycorma delicatula)
This Chinese native feeds on a wide variety of ornamental, fruit, and woody trees. They feed by using their piercing mouthparts to suck sap from their host, weakening the plant.
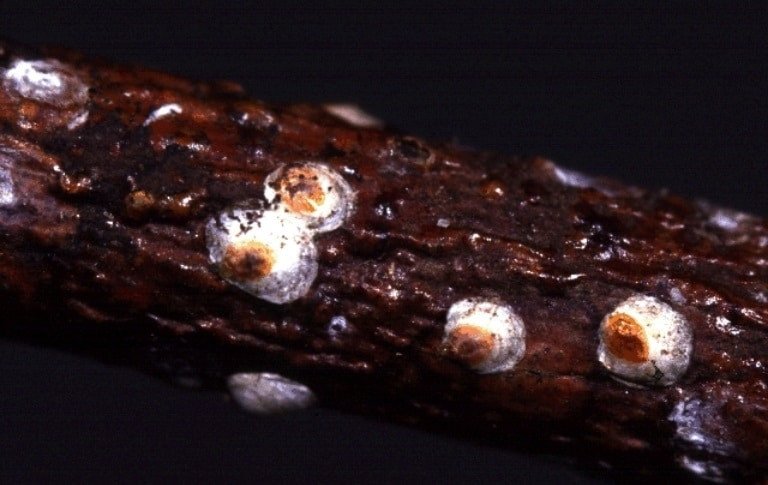

White Peach Scale
(Pseudaulacaspis pentagona)
Originating from either Japan or China, this scale pest has decimated peach orchards throughout New Jersey. Though most prevalent in the southern US, the pest has spread through the northern US as far as Maine.
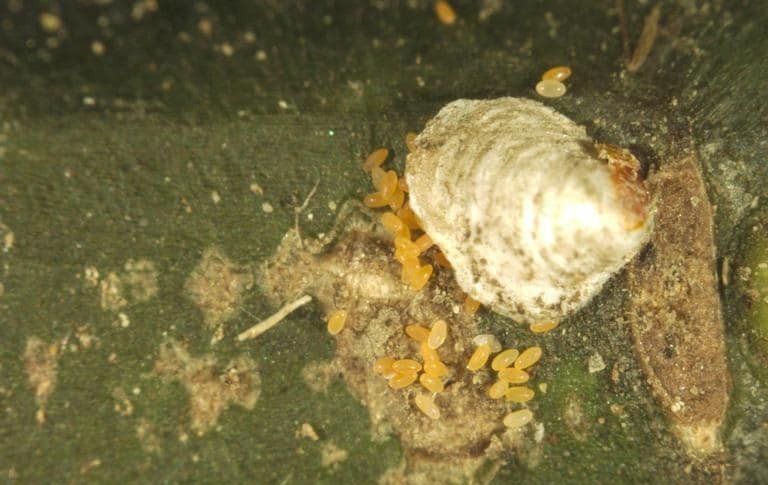

White Prunicola Scale
(Pseudaulacaspis prunicola)
Another invasive species, white prunicola scale have several host species including the cherry laurel and other Prunus species. Light infestations result in leaf yellowing and shedding with heavier infestations causing branch death.
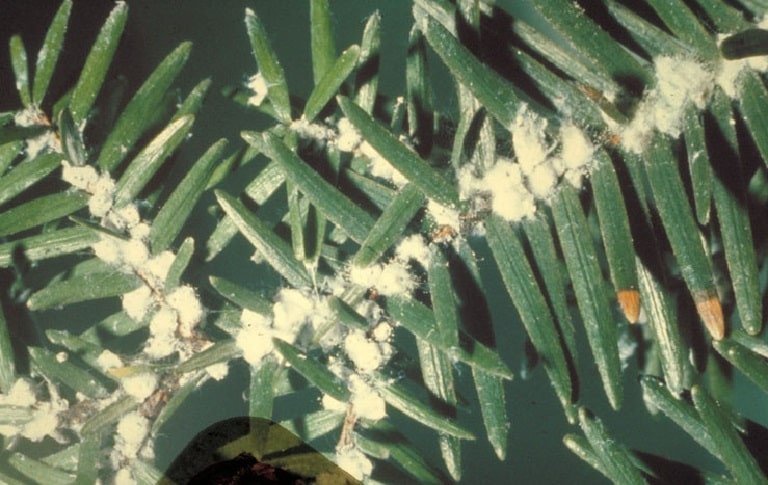

Woolly Adelgid
(Adelges tsugae)
Also known as hemlock woolly adelgid, this invasive insect pest threatens ornamental hemlocks throughout eastern North America. As part of their complex life cycle, immature nymphs settle at the base of hemlock needles and use their sucking mouthparts to feed.
